How to load modes from a FELiCS run and compute structural sensitivity#
Before you start, you should install all necessary FELiCS packages, and install FELiCS as a package itself. The installation guide explains those steps in detail.
After installing FELiCS you can start writing your first FELiCS script.
This tutorial explains how to load previously computed resolvent or eigenmodes from disk using the FELiCS I/O module. The results were saved in the /Input directory. For more information about the initial computation of modal results, see how-to guide 3.
1. Imports and configuration
We begin by importing the necessary FELiCS modules and reading the simulation configuration.
from FELiCS.Parameters.config import config
from FELiCS.Misc.logging import Logger
from FELiCS.IO.Reader import Reader
from FELiCS.Fields.Field import Field
from FELiCS.SpaceDisc.FEMSpaces import FEMSpaces
from FELiCS.Fields.ModeCollection import ModeCollection
import ufl
from FELiCS.Misc.tensorUtils import Tensor, iDot, iConj
🔧 Set up logging and read configuration
logger = Logger(True, False, "felics")
logger = Logger.get_logger("felics")
param = config()
param.importFromFile("Input/config.json")
Debug | logging.py | _setup_logger (line 190 ) : Logger initialized successfully
Debug | config.py | __init__ (line 46 ) : Initializing config class with defaults.
Info | config.py | importFromFile (line 205 ) : Loading configuration from Input/config.json
Warning | config.py | importFromFile (line 224 ) : Field "MolViscPerturbModel" missing from file, setting default: {'type': 'Constant', 'Constants': {'Viscosity': 1.0}}
Warning | config.py | importFromFile (line 224 ) : Field "PrandtlNumber" missing from file, setting default: 0.72
Warning | config.py | importFromFile (line 224 ) : Field "ForcingNorm" missing from file, setting default: TKE
Warning | config.py | importFromFile (line 224 ) : Field "ResponseNorm" missing from file, setting default: TKE
Debug | config.py | importFromFile (line 229 ) : Checking mandatory files
Info | logging.py | change_log_location (line 286 ) : Log files moved to: Input/OutModal/log
Debug | config.py | importFromFile (line 245 ) : Creating Mixture class
Info | MixtureClass.py | __init__ (line 75 ) : No mixture file Mixture.json, using defaults.
Debug | config.py | readDomainData (line 414 ) : Reading domain data from 'Input/CylinderWakeMesh.msh'
Info | FELiCSMesh.py | __init__ (line 94 ) : Opening mesh file: Input/CylinderWakeMesh.msh
Info | FELiCSMesh.py | __init__ (line 102 ) : Mesh contains 3613 nodes and 7224 elements
Info | config.py | importFromFile (line 267 ) : Configuration loaded successfully
This creates:
a global FELiCS logger
a
paramobject that contains all case parameters (mesh path, polynomial order, Reynolds number, etc.), loaded fromconfig.json.
2. Initialization of core FELiCS objects
In this section we reconstruct the essential FELiCS objects exactly as they were used during the mode computation. This ensures consistency of function spaces and mesh mappings.
mesh = param.getMesh()
FELiCS loads the mesh using the path and options specified in config.json.
FEMSpaces = FEMSpaces(param, mesh)
Info | FEMSpaces.py | __init__ (line 132 ) : Defining FEM-spaces.
Debug | FELiCSMesh.py | __init__ (line 381 ) : Initializing refined P1 export mesh.
Debug | FEMSpaces.py | __init__ (line 166 ) : Adding FEM space of order 2 for u
Debug | FEMSpaces.py | __init__ (line 166 ) : Adding FEM space of order 2 for p
Debug | FEMSpaces.py | __init__ (line 184 ) : Mixed finite element list: [blocked element (Basix element (P, triangle, 2, gll_warped, unset, False, float64, []), (2,)), Basix element (P, triangle, 2, gll_warped, unset, False, float64, [])]
This initializes the mixed finite-element space used for the velocity and pressure variables. These spaces must match the ones used when the modes were originally computed.
📥 Initialize the Reader and Writer
reader = Reader(
sourceDir="Input",
needInterpolation=False,
)
The Reader searches the Input/ directory for mode files written by a previous FELiCS run.
3. Loading modes from disk
FELiCS stores modes in an organized modeCollection structure. To load all modes at once, we create an empty ModeCollection and call its importData method.
ModeCollection manages groups of modes, facilitates filtering, and provides utility functions (descriptions, sorting, exporting, etc.).
FELiCS will automatically:
scan the folder
detect available modes (direct and/or adjoint)
reconstruct each mode as a Mode object
rebuild all subfields in the correct function spaces
attach metadata (type, eigenvalue, iteration number, etc.)
importSolution = ModeCollection(
FEMSpaces.VMixed,
mesh
)
importSolution.importData(
reader,
"Input",
)
Info | ModeCollection.py | importData (line 750 ) : Importing 2 modes into mode collection.
Debug | Reader.py | _update_calc_mesh (line 398 ) : New calculation mesh / FEM space type, updating cache.
Debug | Reader.py | clear_cached_properties (line 495 ) : No cached properties to clear.
Debug | Reader.py | importMeshCoords (line 236 ) : Associating import mesh to Reader instance.
Debug | Reader.py | importMeshCoords (line 241 ) : Getting the 2D import mesh coordinates (['x', 'y']).
Debug | Reader.py | _update_data_source (line 347 ) : Reader: switched source to ('/home/demange/repositories/felics2.0/how_tos/11_LoadingModesAndStructuralSensitivity/Input/Mode_Modal_Adjoint_Omega_0.727-0.001j.h5', None), cleared per-file caches.
Debug | Reader.py | importInField (line 885 ) : Cache empty, loading and interpolating/mapping all available data: ['p_imag', 'p_real', 'ux_imag', 'ux_real', 'uy_imag', 'uy_real']
Debug | Reader.py | importInField (line 916 ) : Getting ['ux', 'uy', 'p'] from cached data.
Info | ModeCollection.py | importData (line 784 ) : Imported mode 1/2 from "Mode_Modal_Adjoint_Omega_0.727-0.001j.h5".
Debug | Reader.py | _update_data_source (line 347 ) : Reader: switched source to ('/home/demange/repositories/felics2.0/how_tos/11_LoadingModesAndStructuralSensitivity/Input/Mode_Modal_Direct_Omega_0.727+0.001j.h5', None), cleared per-file caches.
Debug | Reader.py | importInField (line 885 ) : Cache empty, loading and interpolating/mapping all available data: ['p_imag', 'p_real', 'ux_imag', 'ux_real', 'uy_imag', 'uy_real']
Debug | Reader.py | importInField (line 916 ) : Getting ['ux', 'uy', 'p'] from cached data.
Info | ModeCollection.py | importData (line 784 ) : Imported mode 2/2 from "Mode_Modal_Direct_Omega_0.727+0.001j.h5".
🔍 Inspect loaded modes This prints a summary of the imported modes: mode numbers, types, eigenvalues, …
importSolution.describe()
Info | ModeCollection.py | describe (line 69 ) : ModeCollection for AnalysisType.MODAL analysis.
Info | ModeCollection.py | describe (line 70 ) : Contains 2 modes. Contents:
Info | ModeCollection.py | describe (line 74 ) : Mode 0:
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 376 ) : Mode Type: ADJOINT
Warning | Mode.py | guess (line 329 ) : For this mode object no guess was defined. Returning "-9999."...
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 378 ) : Guess: -9999.0
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 379 ) : Eigenvalue: (0.7273431802447646-0.001270747767560071j)
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 386 ) : Wave Number: 0
Info | ModeCollection.py | describe (line 74 ) : Mode 1:
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 376 ) : Mode Type: DIRECT
Warning | Mode.py | guess (line 329 ) : For this mode object no guess was defined. Returning "-9999."...
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 378 ) : Guess: -9999.0
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 379 ) : Eigenvalue: (0.7273431802447553+0.0012707477677050048j)
Info | Mode.py | describe (line 386 ) : Wave Number: 0
4. Extracting specific modes and fields Most analyses involve separating direct and adjoint modes, then selecting individual components of the state vector.
🎯 Separate direct and adjoint modes
directMode = [m for m in importSolution.modeList if m.modeType.name == "DIRECT"][0]
adjointMode = [m for m in importSolution.modeList if m.modeType.name == "ADJOINT"][0]
You can always check:
print(directMode.modeType.name)
DIRECT
🔬 Accessing subfields
FELiCS organizes the mixed state vector hierarchically:
Mode
└── Velocity field
└── Streamwise component (u)
└── Transverse component (v)
└── Pressure
└── … (other fields depending on the model)
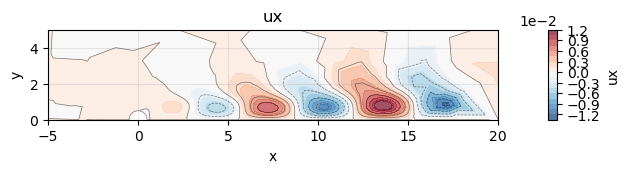
To extract the streamwise velocity:
uxFieldDirect = directMode.getListOfSubFields()[0].getListOfSubFields()[0]
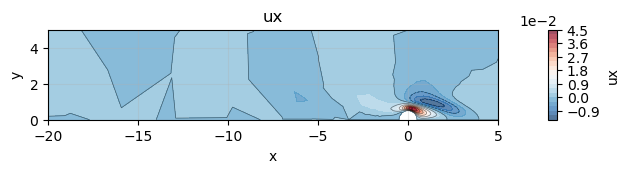
uxFieldAdjoint = adjointMode.getListOfSubFields()[0].getListOfSubFields()[0]
Here:
getListOfSubFields()[0]→ the velocity vector...getListOfSubFields()[0]→ first component, i.e. streamwise velocity
5. Plotting the modes
Each scalar field knows how to plot itself using Matplotlib and the triangulation utilities integrated in FELiCS.
uxFieldDirect.plot(xlim=(-5, 20), ylim=(0, 5))
uxFieldAdjoint.plot(xlim=(-20, 5), ylim=(0, 5))
6. 🌋 Structural Sensitivity in FELiCS
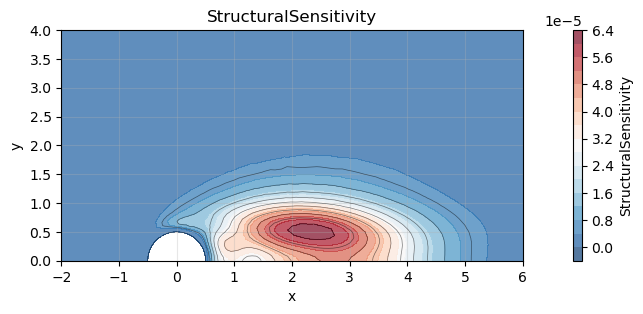
In global stability analysis, the structural sensitivity — often called the wavemaker — identifies the regions in the flow where small changes in the operator have the strongest impact on the eigenvalue. This is precisely the region where an instability is born.
This concept was introduced in the seminal paper: Giannetti & Luchini (2007), “Structural sensitivity of the first instability of the cylinder wake” Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 581: 167–197. doi: 10.1017/S0022112007005654
Their analysis showed that, at the Hopf bifurcation of the cylinder wake, the wavemaker is a compact bubble located just downstream of the cylinder, at the intersection between:
⚡ regions where the direct mode is energetic (perturbation amplification), and
🎯 regions where the adjoint mode is energetic (flow receptivity). Understanding this overlap region is essential for model reduction, flow control, and sensitivity-based design.
📐 (Abbreviated) Mathematical definition Given a direct velocity mode \(u_d(x)\) and the corresponding adjoint mode \(u_a(x)\), the structural sensitivity tensor is
🛠️ How to evaluate tensor expressions in FELiCS (essentials)
evaluateUflTensorExpression is a compact but powerful FELiCS routine that evaluates any tensor-based UFL expression and stores the result in a Field. It is the recommended way to compute derived quantities (e.g. structural sensitivity, vorticity, energy norms) because it:
✔ Uses the FELiCS tensor framework: The expression is interpreted using
Tensor,iDot,iConj, and the coordinate-system JacobianJ_hat, ensuring that all operators follow the correct physics, including non-Cartesian coordinate systems and spectral directions. (A pure-ufl version of this function exist withevaluateUflExpression)✔ Automatically assembles a consistent weak form: The method builds the appropriate “mass-like” variational form for the field’s function space, assembles it once, and stores the corresponding LU solver for reuse.
✔ Efficiently evaluates and inserts the result: The input expression is assembled into a vector, solved with the precomputed solver, and the field’s coefficient array is updated.
✔ Ideal for post-processing: You can turn complex mathematical expressions directly into FEM fields with one line, without manually writing projection operators or variational problems.
🧠 Structural sensitivity in FELiCS FELiCS uses a tensor-aware framework for field representation. This allows us to compute expressions like structural sensitivity in a coordinate-system consistent way.
The computational steps are:
🔍 Extract the direct and adjoint velocity fluctuation fields.
🧮 Choose a scalar FE space \(V\) to store the sensitivity.
✏️ Build the appropriate UFL tensor expression
⚙️ Assemble the expression using
evaluateUflTensorExpression.🎨 Plot the resulting scalar field.
🧩 FELiCS implementation
# --- Extract direct and adjoint velocity fields -----------------------
uFieldDirect = directMode.getListOfSubFields()[0] # velocity fluctuation
uFieldAdjoint = adjointMode.getListOfSubFields()[0]
# --- Test space where the scalar sensitivity will live ---------------
V_scalar = FEMSpaces.P2
v = ufl.TestFunction(V_scalar)
# --- Create empty field to store structural sensitivity --------------
sS = Field(V_scalar, mesh)
sS.name = "StructuralSensitivity"
# --- Build the UFL tensor expression ---------------------------------
J_hat = sS.mesh.coordinateSystem.J_hat
v_tens = Tensor(
v,
CoordSys=sS.mesh.coordinateSystem,
m=sS.m,
mayHaveSpectralDimension=sS.hasSpectralDimension,
)
exprSS = (
iDot(uFieldDirect.getTensor(), iConj(uFieldDirect.getTensor()))**0.5 *
iDot(uFieldAdjoint.getTensor(), iConj(uFieldAdjoint.getTensor()))**0.5 *
iConj(v_tens)
).ufl_tens * J_hat * ufl.dx
# --- Evaluate expression and build the finite-element field -----------
sS.evaluateUflTensorExpression(exprSS)
🎨 Plotting the result
sS.plot(xlim=(-2, 6), ylim=(0, 4))