How to calculate the L2-norm of a field#
Step 1: Create FELiCSMesh, FELiCSSpace and Field
from FELiCS.SpaceDisc.FELiCSMesh import FELiCSMesh
from FELiCS.SpaceDisc.FEMSpaces import createFunctionSpace
from FELiCS.Fields.Field import Field
from FELiCS.IO.Reader import Reader
meshFileName = "./square_mesh.msh"
coordinateSystemName = "Cartesian"
# Create a FELiCS mesh from the gmsh file
mesh = FELiCSMesh(coordinateSystemName=coordinateSystemName, meshFileName=meshFileName)
scalarSpace = createFunctionSpace(mesh, degree=2, dim=1)
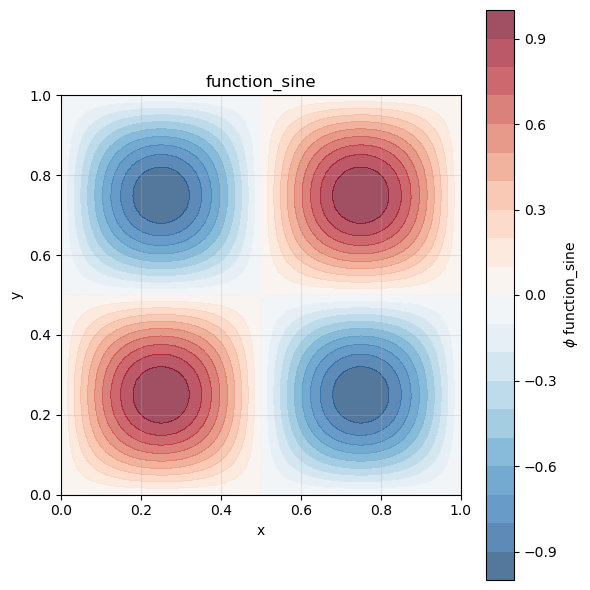
phi = Field(scalarSpace, mesh=mesh, name="function_sine")
phi.importData(Reader(),"input.h5")
phi.plot()
Info | FELiCSMesh.py | __init__ (line 75 ) : Opening mesh file: ./square_mesh.msh
Info | FELiCSMesh.py | __init__ (line 83 ) : Mesh contains 513 nodes and 1024 elements
Step 2: Calculate the L2-norm of a field
Now we will calculate an integral quantity of our field. We will calculate the L2-norm of our field over the whole domain.
The L2-norm is defined as:
\[||\phi(\mathbf{x})||_{L^2} = \sqrt{\int_\Omega |\phi(\mathbf{x})|^2 \, d\Omega}\]
For this, the Field class has the method calculateL2Norm() which computes this integral over the entire mesh domain.
u_norm = phi.calculateL2Norm()
print(f"L2-norm of the field: {u_norm}")
L2-norm of the field: (0.49952523537468385+0j)
